MongoDB
MongoDB 的核心优势
- 灵活模式 json 文档
- 高可用性 副本集
- 可扩展性 sharded cluster 分片集群,可以将数据分散存储到多个分片 shard 上来实现高扩展性。
使 MongoDB 具备了横向扩展的能力。
部署方式
- 主从复制 master-slave ,目前不推荐使用了。
- 副本集 replica set,将数据复制多份,不同服务器保存同一份数据,在出现故障时自动切换,实现故障转移。
- 分片模式 sharding,适合处理大量数据,它将数据分开存储,不同的服务器保存不同的数据,所有服务器数据的总和即为整个数据集。(* 追求高性能*)

https://www.cnblogs.com/yanxinjiang/p/14600568.html
https://zhangquan.me/2023/03/26/mongodb-fen-pian-ji-qun-ji-zhi-ji-yuan-li/
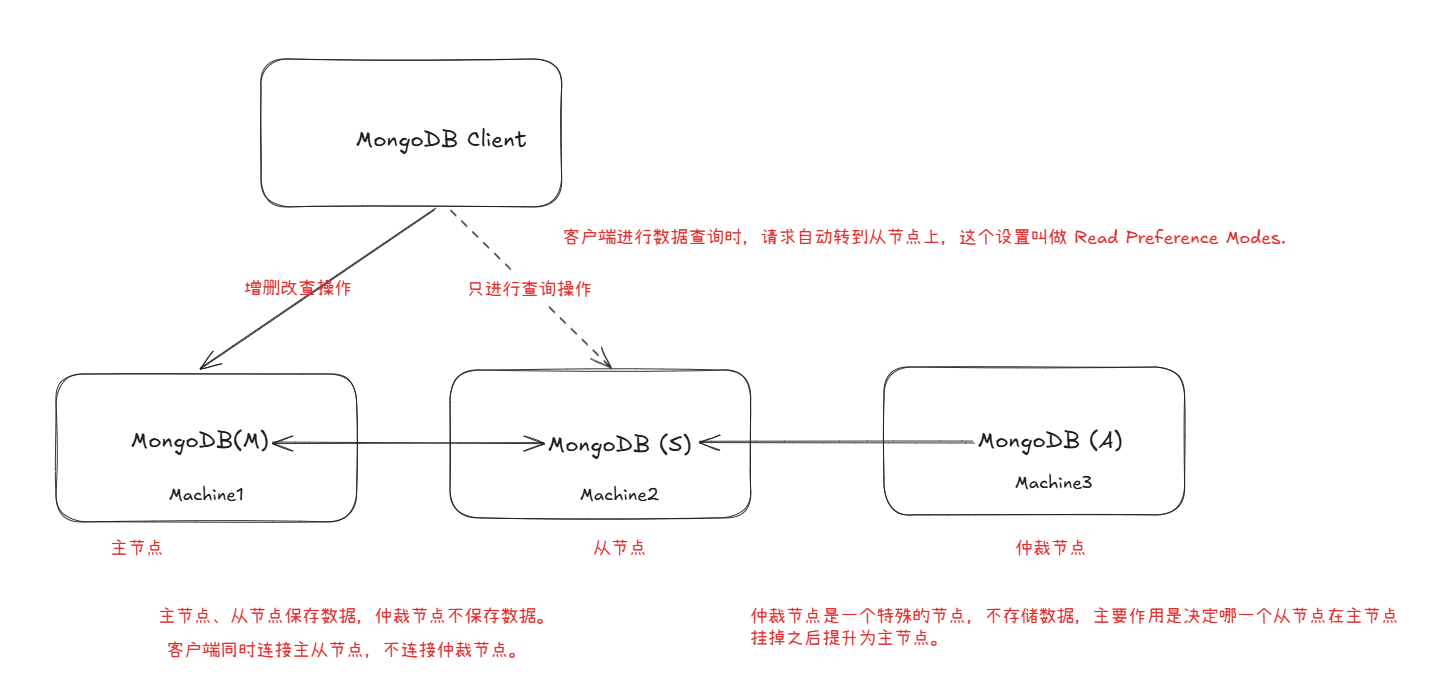
副本集部署方式
增删改查基本操作
- Adhoc queries 临时查询
- Data transformations 数据转换
- Document join support 文档连接
$lookup$unionwith - Graph and geospatial queries 图形和地理空间查询
$geoWithin$geoNeargraphLookup - Full-text search 全文检索
$search - Semantic search 语义搜索
$vectorSearch - Indexing 索引
- On-demand materialized views 按需创建实体索引
$out$merge - Time series analysis 时间序列分析
1. 查询数据库列表
db.adminCommand({ listDatabases: 1 });
2. $unwind
db.inventory.insertMany( [
{ prodId: 100, price: 20, quantity: 125 },
{ prodId: 101, price: 10, quantity: 234 },
{ prodId: 102, price: 15, quantity: 432 },
{ prodId: 103, price: 17, quantity: 320 }
] );
db.orders.insertMany( [
{ orderId: 201, custid: 301, prodId: 100, numPurchased: 20 },
{ orderId: 202, custid: 302, prodId: 101, numPurchased: 10 },
{ orderId: 203, custid: 303, prodId: 102, numPurchased: 5 },
{ orderId: 204, custid: 303, prodId: 103, numPurchased: 15 },
{ orderId: 205, custid: 303, prodId: 103, numPurchased: 20 },
{ orderId: 206, custid: 302, prodId: 102, numPurchased: 1 },
{ orderId: 207, custid: 302, prodId: 101, numPurchased: 5 },
{ orderId: 208, custid: 301, prodId: 100, numPurchased: 10 },
{ orderId: 209, custid: 303, prodId: 103, numPurchased: 30 }
] );
// 根据 orders 创建 sales 集合
db.createView("sales", "orders", [
{
$lookup: // 使用 orders.prodId 匹配 inventory.prodId
{
from: "inventory",
localField: "prodId",
foreignField: "prodId",
as: "inventoryDocs" // 匹配到的数据添加到 inventoryDocs 集合中
}
},
{
$project: // 选择显示的字段
{
_id: 0, // 不显示
prodId: 1, // 显示
orderId: 1,
numPurchased: 1,
price: "$inventoryDocs.price" // 聚合成 price 字段(数组)
}
},
{
$unwind: "$price" // 将数组展开
}
]);
$unwind 的作用: 展开数组字段
假设 collection 的数据如下所示
[
{ "_id": 1, "product": "A", "price": [100, 200, 300] },
{ "_id": 2, "product": "B", "price": [400, 500] },
{ "_id": 3, "product": "C", "price": [] },
{ "_id": 4, "product": "D" }
]
在使用 $unwind 函数之后
[
{ "_id": 1, "product": "A", "price": 100 },
{ "_id": 1, "product": "A", "price": 200 },
{ "_id": 1, "product": "A", "price": 300 },
{ "_id": 2, "product": "B", "price": 400 },
{ "_id": 2, "product": "B", "price": 500 }
]
3. 创建视图,并排序
db.places.insertMany([
{ _id: 1, category: "café" },
{ _id: 2, category: "cafe" },
{ _id: 3, category: "cafE" }
]);
db.places.find();
根据 places 创建视图 placesView , 只保留 category 字段,并且根据 fr 进行排序
db.createView(
"placesView",
"places",
[{
$project: {
category: 1
}
}],
{
collation: {
locale: "fr", // 指定语言环境为 法语
strength: 1 // 排序强度, 1 表示只比较基本字符.
}
}
);
统计 category = cafe 的文档数量
db.placesView.countDocuments({
category: "cafe"
});
4. 视图修改
先删除,再新建
db.createView("places-view-modify", "places", [
{
$match: {
category: "cafe"
}
}
]);
db["places-view-modify"].find();
db["places-view-modify"].drop();
直接修改视图
db.runCommand(
{
collMod: "places-view-modify",
viewOn: "places",
"pipeline": [{
$match: {
category: "cafE"
}
}]
}
);
5. 物化视图
// 物化视图 $merge $out 的结果
db.bakesales.insertMany( [
{ date: new ISODate("2018-12-01"), item: "Cake - Chocolate", quantity: 2, amount: new NumberDecimal("60") },
{ date: new ISODate("2018-12-02"), item: "Cake - Peanut Butter", quantity: 5, amount: new NumberDecimal("90") },
{ date: new ISODate("2018-12-02"), item: "Cake - Red Velvet", quantity: 10, amount: new NumberDecimal("200") },
{ date: new ISODate("2018-12-04"), item: "Cookies - Chocolate Chip", quantity: 20, amount: new NumberDecimal("80") },
{ date: new ISODate("2018-12-04"), item: "Cake - Peanut Butter", quantity: 1, amount: new NumberDecimal("16") },
{ date: new ISODate("2018-12-05"), item: "Pie - Key Lime", quantity: 3, amount: new NumberDecimal("60") },
{ date: new ISODate("2019-01-25"), item: "Cake - Chocolate", quantity: 2, amount: new NumberDecimal("60") },
{ date: new ISODate("2019-01-25"), item: "Cake - Peanut Butter", quantity: 1, amount: new NumberDecimal("16") },
{ date: new ISODate("2019-01-26"), item: "Cake - Red Velvet", quantity: 5, amount: new NumberDecimal("100") },
{ date: new ISODate("2019-01-26"), item: "Cookies - Chocolate Chip", quantity: 12, amount: new NumberDecimal("48") },
{ date: new ISODate("2019-01-26"), item: "Cake - Carrot", quantity: 2, amount: new NumberDecimal("36") },
{ date: new ISODate("2019-01-26"), item: "Cake - Red Velvet", quantity: 5, amount: new NumberDecimal("100") },
{ date: new ISODate("2019-01-27"), item: "Pie - Chocolate Cream", quantity: 1, amount: new NumberDecimal("20") },
{ date: new ISODate("2019-01-27"), item: "Cake - Peanut Butter", quantity: 5, amount: new NumberDecimal("80") },
{ date: new ISODate("2019-01-27"), item: "Tarts - Apple", quantity: 3, amount: new NumberDecimal("12") },
{ date: new ISODate("2019-01-27"), item: "Cookies - Chocolate Chip", quantity: 12, amount: new NumberDecimal("48") },
{ date: new ISODate("2019-01-27"), item: "Cake - Carrot", quantity: 5, amount: new NumberDecimal("36") },
{ date: new ISODate("2019-01-27"), item: "Cake - Red Velvet", quantity: 5, amount: new NumberDecimal("100") },
{ date: new ISODate("2019-01-28"), item: "Cookies - Chocolate Chip", quantity: 20, amount: new NumberDecimal("80") },
{ date: new ISODate("2019-01-28"), item: "Pie - Key Lime", quantity: 3, amount: new NumberDecimal("60") },
{ date: new ISODate("2019-01-28"), item: "Cake - Red Velvet", quantity: 5, amount: new NumberDecimal("100") },
] );
db.bakesales.find();
// 定义了一个包含每月累计销售信息的物化视图
updateMonthlySales = function(startDate) {
db.bakesales.aggregate([
{
$match: {
date: {
$gte: startDate // 大于等于传入的日期的数据
}
}
},
{
$group: {
_id: {
$dateToString: { // 根据 date 字段的 %Y-%m 进行分组
format: "%Y-%m",
date: "$date"
}
},
sales_quantity: {
$sum: "$quantity" // 新增一个 sales_quantity 字段
},
sales_amount: {
$sum: "$amount" // 新增 sales_amount 字段
}
}
},
{
$merge: {
into: "monthlybakesales", // 将数据输出到 monthlybakesales 集合中
whenMatched: "replace" // 当文档已经存在于目的集合时,替换目的集合中的文档
}
}
]);
};
updateMonthlySales(new ISODate("1970-01-01"));
db.monthlybakesales.find();
更新物化视图
db.bakesales.insertMany( [
{ date: new ISODate("2019-01-28"), item: "Cake - Chocolate", quantity: 3, amount: new NumberDecimal("90") },
{ date: new ISODate("2019-01-28"), item: "Cake - Peanut Butter", quantity: 2, amount: new NumberDecimal("32") },
{ date: new ISODate("2019-01-30"), item: "Cake - Red Velvet", quantity: 1, amount: new NumberDecimal("20") },
{ date: new ISODate("2019-01-30"), item: "Cookies - Chocolate Chip", quantity: 6, amount: new NumberDecimal("24") },
{ date: new ISODate("2019-01-31"), item: "Pie - Key Lime", quantity: 2, amount: new NumberDecimal("40") },
{ date: new ISODate("2019-01-31"), item: "Pie - Banana Cream", quantity: 2, amount: new NumberDecimal("40") },
{ date: new ISODate("2019-02-01"), item: "Cake - Red Velvet", quantity: 5, amount: new NumberDecimal("100") },
{ date: new ISODate("2019-02-01"), item: "Tarts - Apple", quantity: 2, amount: new NumberDecimal("8") },
{ date: new ISODate("2019-02-02"), item: "Cake - Chocolate", quantity: 2, amount: new NumberDecimal("60") },
{ date: new ISODate("2019-02-02"), item: "Cake - Peanut Butter", quantity: 1, amount: new NumberDecimal("16") },
{ date: new ISODate("2019-02-03"), item: "Cake - Red Velvet", quantity: 5, amount: new NumberDecimal("100") }
]);
updateMonthlySales(new ISODate("2019-01-01"));
6. capped collections
capped collections: 固定大小的集合。
db.createCollection("log", {
capped: true,
size: 100000 // 最大大小为 100000 的集合 ( mongodb 会四舍五入到最接近 256 的整数倍)
});
db.createCollection(
"log2",
{
capped: true,
size: 5242880,
max: 5000 // 文档数最大为 5000
}
);
db.log.insertMany( [
{
message: "system start",
type: "startup",
time: 1711403508
},
{
message: "user login attempt",
type: "info",
time: 1711403907
},
{
message: "user login fail",
type: "warning",
time: 1711404209
},
{
message: "user login success",
type: "info",
time: 1711404367
},
{
message: "user logout",
type: "info",
time: 1711404555
}
] )
db.log.find();
db.log.find({
type: "info"
});
db.log.find().sort({
$natural: - 1 // 与插入的顺序相反
});
判断集合是否为capped collections
db.log.isCapped();
修改限制
db.runCommand( { collMod: "log", cappedSize: 5242880 } )
db.runCommand( { collMod: "log", cappedMax: 5000 } )
7. null 与 undefined
MongoDB 8.0 之后,null 的比较不会匹配 undefined。
db.people.insertMany([
{
_id: 1,
name: null
},
{
_id: 2,
name: undefined
},
{
_id: 3,
name: ["Gabriel", undefined]
},
{
_id: 4,
names: ["Alice", "Charu"] // 注意,这里是 names ,不是 name
}
]);
db.people.find();
db.people.find({
name: null
}); // v8.0 之后,只匹配 null 和 name 不存在的数据. 即 id = 1 and id = 4
// 删除 name 字段中包含 undefined 的文档
db.people.updateMany(
{
name: {
$type: "undefined"
}
},
[{
$set: {
"name": {
$cond: {
// When "name" is an array, convert { name: [ "Alice", undefined ] }
// to { name: [ "Alice" ] }
if : {
$eq: [{
$type: "$name"
}, "array"]
},
then: {
$filter: {
input: "$name",
cond: {
$not: {
$eq: [{
$type: "$$this"
}, "undefined"]
}
}
},
},
// When "name" is scalar undefined, remove it
else : "$$REMOVE"
}
}
}
}]
);
db.people.updateMany( // 批量更新
{ },
[ {
$replaceWith: { // 集合更新管道,替换文档的根节点, 接受一个文档作为参数
$arrayToObject: { // $arrayToObject + $filter 生成不包含 undefined 字段的文档
$filter: {
input: { $objectToArray: "$$ROOT" }, // 讲文档的每个字段转为键值对的数组形式
cond: {
$not: { $eq: [ { $type: "$$this.v" }, "undefined" ] } // 检查 this.v 是否为 undefined
}
}
}
}
} ]
)
db.people.updateMany(
{ name: { $type: "undefined" } },
[ {
$set: {
"name": {
$cond: {
// When "name" is an array, convert { name: [ "Alice", undefined ] }
// to { name: [ "Alice", null ] }
if: {
$eq: [ { $type: "$name" }, "array" ]
},
then: {
$map: {
input: "$name",
in: {
$cond: {
if: { $eq: [ { $type: "$$this" }, "undefined" ] },
then: null,
else: "$$this"
}
}
},
},
// When "name" is the scalar undefined, convert to null
else: null
}
}
}
} ]
)
8. insert
db.inventory.insertOne(
{
item: "canvas",
qty: 100,
tags: ["cotton"],
size: {
h: 28,
w: 35.5,
uom: "cm"
}
}
);
db.inventory.find();
db.inventory.insertMany([
{ item: "journal", qty: 25, tags: ["blank", "red"], size: { h: 14, w: 21, uom: "cm" } },
{ item: "mat", qty: 85, tags: ["gray"], size: { h: 27.9, w: 35.5, uom: "cm" } },
{ item: "mousepad", qty: 25, tags: ["gel", "blue"], size: { h: 19, w: 22.85, uom: "cm" } }
])
db.inventory.insertMany([
{ item: "journal", qty: 25, size: { h: 14, w: 21, uom: "cm" }, status: "A" },
{ item: "notebook", qty: 50, size: { h: 8.5, w: 11, uom: "in" }, status: "A" },
{ item: "paper", qty: 100, size: { h: 8.5, w: 11, uom: "in" }, status: "D" },
{ item: "planner", qty: 75, size: { h: 22.85, w: 30, uom: "cm" }, status: "D" },
{ item: "postcard", qty: 45, size: { h: 10, w: 15.25, uom: "cm" }, status: "A" }
]);
9. select
// status = 'D'
db.inventory.find({
status: "D"
});
// status in ('A','D')
db.inventory.find({
status: {
$in: ["A", "D"]
}
});
// status = 'A' and qty < 30
db.inventory.find({
status: "A",
qty: {
$lt: 30
}
});
// status = 'A' or qty < 30
db.inventory.find({
$or: [{
status: "A"
}, {
qty: {
$lt: 30
}
}]
});
// status = 'A' and (qty < 30 or item like 'p%')
db.inventory.find({
status: "A",
$or: [{
qty: {
$lt: 30
}
}, {
item: /^p/
}]
})
// embedded document
db.inventory.insertMany( [
{ item: "journal", qty: 25, size: { h: 14, w: 21, uom: "cm" }, status: "A" },
{ item: "notebook", qty: 50, size: { h: 8.5, w: 11, uom: "in" }, status: "A" },
{ item: "paper", qty: 100, size: { h: 8.5, w: 11, uom: "in" }, status: "D" },
{ item: "planner", qty: 75, size: { h: 22.85, w: 30, uom: "cm" }, status: "D" },
{ item: "postcard", qty: 45, size: { h: 10, w: 15.25, uom: "cm" }, status: "A" }
]);
db.inventory.find({
"size.uom": "in"
});
db.inventory.find({
"size.h": {
$lt: 15
}
});
// size.w = 21 and size.h = 14 and size.uom = 'cm'
db.inventory.find({
size: {
w: 21,
h: 14,
uom: "cm"
}
});
// arrays
db.inventory.insertMany([
{ item: "journal", qty: 25, tags: ["blank", "red"], dim_cm: [ 14, 21 ] },
{ item: "notebook", qty: 50, tags: ["red", "blank"], dim_cm: [ 14, 21 ] },
{ item: "paper", qty: 100, tags: ["red", "blank", "plain"], dim_cm: [ 14, 21 ] },
{ item: "planner", qty: 75, tags: ["blank", "red"], dim_cm: [ 22.85, 30 ] },
{ item: "postcard", qty: 45, tags: ["blue"], dim_cm: [ 10, 15.25 ] }
]);
// tags = ["red","blank"]
db.inventory.find({
tags: ["red", "blank"]
});
// tags contains ["red","blank"]
db.inventory.find({
tags: {
$all: ["red", "blank"]
}
});
// 'red' in tags
db.inventory.find({
tags: "red"
});
// dim_cm 存在大于 25 的元素
db.inventory.find({
dim_cm: {
$gt: 25
}
});
// dim_cm 存在大于 15 小于 20 的元素
db.inventory.find({
dim_cm: {
$gt: 15,
$lt: 20
}
});
// dim_cm 的第 2 个元素大于 25
db.inventory.find({
"dim_cm.1": {
$gt: 25
}
});
// tags.length = 3
db.inventory.find({
"tags": {
$size: 3
}
});
// arrays of embeeded documents
db.inventory.insertMany( [
{ item: "journal", instock: [ { warehouse: "A", qty: 5 }, { warehouse: "C", qty: 15 } ] },
{ item: "notebook", instock: [ { warehouse: "C", qty: 5 } ] },
{ item: "paper", instock: [ { warehouse: "A", qty: 60 }, { warehouse: "B", qty: 15 } ] },
{ item: "planner", instock: [ { warehouse: "A", qty: 40 }, { warehouse: "B", qty: 5 } ] },
{ item: "postcard", instock: [ { warehouse: "B", qty: 15 }, { warehouse: "C", qty: 35 } ] }
]);
instock.warehouse = 'A' and instock.qty = 5 (需要顺序一致)
db.inventory.find({
"instock": {
warehouse: "A",
qty: 5
}
});
// instock.qty = 5 and instock.warehouse = 'A'
db.inventory.find({
"instock": {
qty: 5,
warehouse: "A"
}
});
// instock.qty <= 20
db.inventory.find({
'instock.qty': {
$lte: 20
}
});
// instock[0].qty <= 20
db.inventory.find({
'instock.0.qty': {
$lte: 20
}
});
// instock contains {qty: 5, warehouse: 'A'}
db.inventory.find({
"instock": {
$elemMatch: { // 不匹配顺序
qty: 5,
warehouse: "A"
}
}
});
// instock contains { 10 < qty <= 20 }
db.inventory.find({
"instock": {
$elemMatch: {
qty: {
$gt: 10,
$lte: 20
}
}
}
});
// instock.qty = 5 and instock.warehouse = 'A'
db.inventory.find({
"instock.qty": 5,
"instock.warehouse": "A"
})
指定返回字段
// project results
db.inventory.insertMany( [
{ item: "journal", status: "A", size: { h: 14, w: 21, uom: "cm" }, instock: [ { warehouse: "A", qty: 5 } ] },
{ item: "notebook", status: "A", size: { h: 8.5, w: 11, uom: "in" }, instock: [ { warehouse: "C", qty: 5 } ] },
{ item: "paper", status: "D", size: { h: 8.5, w: 11, uom: "in" }, instock: [ { warehouse: "A", qty: 60 } ] },
{ item: "planner", status: "D", size: { h: 22.85, w: 30, uom: "cm" }, instock: [ { warehouse: "A", qty: 40 } ] },
{ item: "postcard", status: "A", size: { h: 10, w: 15.25, uom: "cm" }, instock: [ { warehouse: "B", qty: 15 }, { warehouse: "C", qty: 35 } ] }
]);
// status = 'A'
db.inventory.find( { status: "A" } )
// select _id,item , status from inventory where status = 'A'
db.inventory.find( { status: "A" }, { item: 1, status: 1 } );
// select item , status from inventory where status = 'A'
db.inventory.find( { status: "A" }, { item: 1, status: 1, _id: 0 } )
// 不显示 status instock 字段
db.inventory.find( { status: "A" }, { status: 0, instock: 0 } )
// 返回 item status size.uom 字段
db.inventory.find(
{
status: "A"
},
{
item: 1,
status: 1,
"size.uom": 1
}
)
db.inventory.find({
status: "A"
});
// 返回 item status instock.qty 字段
db.inventory.find({
status: "A"
}, {
item: 1,
status: 1,
"instock.qty": 1
});
分支条件
db.inventory.find(
{},
{
_id: 0,
item: 1,
status: {
$switch: { // 分支条件 $switch + branches + default 一起使用
branches: [
{
case: {
$eq: ["$status", "A"]
},
then: "Available"
},
{
case: {
$eq: ["$status", "D"]
},
then: "Discontinued"
},
],
default: "No status found"
}
},
area: { // $size.h * $size.w + " " + $size.uom
$concat: [
{
$toString: {
$multiply: ["$size.h", "$size.w"]
}
},
" ",
"$size.uom"
]
},
reportNumber: {
$literal: 1 // $literal 是一个特殊运算符,用于返回一个常量值(即字面值),它的作用是将提供的值直接作为结果输出,而不会被解释为字段或表达式。
}
}
);
10. $literal
$literal 是一个特殊运算符,用于返回一个常量值(即字面值),它的作用是将提供的值直接作为结果输出,而不会被解释为字段或表达式。
db.inventory.aggregate([
{
$project:
{
aa: {
$literal: 1
}
}
}
]);
11. $exist
查找不存在 item 的字段
db.inventory.find({
item: {
$exists: false
}
});
12. $currentDate
将字段的值设置为当前日期。
db.customers.updateOne(
{ _id: 1 },
{
$currentDate: {
lastModified: true, // 将 lastModified 字段修改为当前时间
"cancellation.date": { $type: "timestamp" } // 将 cancellation.date 修改为当前时间戳
},
$set: {
"cancellation.reason": "user request", // 将 cancellation.reason 修改为 user request
status: "D" // 将 status 修改为 D
}
}
);
聚合方式
聚合变量需要使用$$ ,并且使用双引号。eg: "$$NOW"
db.customers.updateOne(
{
_id: 1
},
[
{
$set: {
lastModified: "$$NOW", // 聚合变量需要使用 $$ ,并且使用双引号。
cancellation: {
date: "$$CLUSTER_TIME", // 时间戳
reason: "user request"
},
status: "D"
}
}
]
);
13. 更新文档
- updateOne: 修改单个文档
db.inventory.updateOne(
{ item: "paper" },
{
$set: { "size.uom": "cm", status: "P" },
$currentDate: { lastModified: true }
}
)
- updateMany: 修改多个文档
db.inventory.updateMany(
{ "qty": { $lt: 50 } },
{
$set: { "size.uom": "in", status: "P" },
$currentDate: { lastModified: true }
}
)
- replaceOne: 替换
_id字段之外的整个文档内容。
db.inventory.replaceOne(
{ item: "paper" },
{ item: "paper", instock: [ { warehouse: "A", qty: 60 }, { warehouse: "B", qty: 40 } ] }
)
14. $set
db.students.updateOne({
_id: 3
}, [{
$set: {
"test3": 98,
modified: "$$NOW"
}
}]);
15. $mergeObjects
$mergeObjects 合并多个对象为一个对象,相同的字段以最后一个对象为准。
db.students2.updateMany({}, [
{
$replaceRoot: {
// 新增一个文档,因为第一个参数是 {}
newRoot:
{
$mergeObjects: [{ // $mergeObjects 合并多个对象为一个对象,相同的字段以最后一个对象为准。
quiz1: 0,
quiz2: 0,
test1: 0,
test2: 0
}, "$$ROOT"]
}
}
},
{
$set: {
modified: "$$NOW"
}
}
]);
16. $replaceRoot
用于替换文档的根内容,即完全替换当前文档的顶层结构为一个新的结构。
17. $trunc
$trunc 是一个算术运算符,用于截断数字的小数部分,保留指定位数小数。不会四��舍五入
db.students3.updateMany(
{}, // 会匹配到所有字段
[
{
$set: {
average: { // 新增一个 average 字段
$trunc: [{ // 截断小数,保留指定位数,此处保留 0 位小数
$avg: "$tests"
}, 0]
},
modified: "$$NOW"
}
},
{
$set: {
grade: {
$switch: {
branches: [
{
case: { // >= 90 A
$gte: ["$average", 90]
},
then: "A"
},
{
case: { // >= 80 B
$gte: ["$average", 80]
},
then: "B"
},
{
case: { // >= 70 C
$gte: ["$average", 70]
},
then: "C"
},
{
case: { // >= 60 D
$gte: ["$average", 60]
},
then: "D"
}
],
default: "F"
}
}
}
}
]
)
18. $concatArrays
$concatArrays 是一个用于将两个或多个数组连接在一起的操作符。
db.students4.updateOne({
_id: 2
}, [{
$set: {
quizzes: {
$concatArrays: ["$quizzes", [8, 6]]
}
}
}]);
19. $map
{ $map: { input: <expression>, as: <string>, in: <expression> } }
20. 删除文档
db.inventory.find();
db.inventory.insertMany( [
{ item: "journal", qty: 25, size: { h: 14, w: 21, uom: "cm" }, status: "A" },
{ item: "notebook", qty: 50, size: { h: 8.5, w: 11, uom: "in" }, status: "P" },
{ item: "paper", qty: 100, size: { h: 8.5, w: 11, uom: "in" }, status: "D" },
{ item: "planner", qty: 75, size: { h: 22.85, w: 30, uom: "cm" }, status: "D" },
{ item: "postcard", qty: 45, size: { h: 10, w: 15.25, uom: "cm" }, status: "A" },
] );
db.inventory.deleteMany({}); // 删除集合中所有文档
db.inventory.deleteMany({ status : "A" }) // 删除 status = 'A'
db.inventory.deleteOne( { status: "D" } ) // 删除 status ='D' 的第一个文档
// 1. 不会丢弃索引
// 2. 单个文档的操作是原子性的
// 3. write concern
21. Write Concern 写入确认级别
写操作的确认策略和数据持久化级别的一组配置。
w: 定义需要确认写入的节点数量或策略。
- 开发和测试环境
w:0或w:1- 一般业务系统:
w: majority或w: 2~3- 金融系统:
w: majority and j: true会显著的降低写操作的性能,需要权衡写入速度和可靠性。
j:是否等待数据持久化到磁盘 (journal 文件)
wtimeoutMS:等待写操作确认的超时时间。
db.collection.insertOne(
{ name: "Alice", age: 25 },
{ writeConcern: { w: "majority", j: true } }
);
majority
- 写入数据必须被直接点持久化到内存中。
- 被副本集中大多数节点确认完成 (
N/2 + 1)- 副本集有 3 个节点, majority = 2
- 副本集有 5 个节点, majority = 3
22. Bulk Write
try {
db.pizzas.bulkWrite( [
{ insertOne: { document: { _id: 3, type: "beef", size: "medium", price: 6 } } },
{ insertOne: { document: { _id: 4, type: "sausage", size: "large", price: 10 } } },
{ updateOne: {
filter: { type: "cheese" },
update: { $set: { price: 8 } }
} },
{ deleteOne: { filter: { type: "pepperoni"} } },
{ replaceOne: {
filter: { type: "vegan" },
replacement: { type: "tofu", size: "small", price: 4 }
} }
] )
} catch( error ) {
print( error )
}
Ordered,默认 true
有序:其中一个写操作失败,剩余的写操作不会执行。
无序:其中一个写操作时发生错误,MongoDB 会继续处理列表中剩余的写操作。
db.collection.bulkWrite(
[
{ insertOne : <document> },
{ updateOne : <document> },
{ updateMany : <document> },
{ replaceOne : <document> },
{ deleteOne : <document> },
{ deleteMany : <document> }
],
{ ordered : false } // 默认有序。
)
分片集合的批量插入
- 预分割集合 Pre-Split the Collection
- 无序写入到 mongos Unordered Writes to mongos
- 避免单调 Avoid Monotonic Throttling
23. Retryable Writes 可重试写入
mongosh --retryWrites=true
Prerequisites:
- 需要副本集或分片集群,不支持独立实例。
- 需要支持文档级锁定的存储引擎,例如 WiredTiger 或内存存储引擎。
- MongoDB 3.6+
- Write Concern 的
w不为0,0表示不重试
24. Retryable Reads 可重试读取
MongoDB Server 4.2+
25. Geospatial Queries 地理空间搜索
<field>: { type: <GeoJSON type> , coordinates: <coordinates> }
先 longitude 经度(-180,180) ,后 latitude 维度(-90,90)。
location: {
type: "Point",
coordinates: [-73.856077, 40.848447]
}
Legacy Coordinate Paris 传统坐标对
- 数组指定:
<field>: [ <x>, <y> ] - 文档嵌入:
<field>: { <field1>: <x>, <field2>: <y> }
26. Read Concern
readConcern 选项,可以控制从 replica sets 和 sharded clusters 读取的数据的 一致性 consistency 和 隔离性
isolation。
在执行 find 或者 aggregate 时,可以通过 readConcern 来把控返回数据的准确性和可靠性。
Read Concern Levels 读关注级别
read concern 决定了查询返回的数据的一致性级别。它指定了查询应返回的数据版本。
MongoDB 支持的 Read Concern 级别
local(default)availablemajoritylinearizablesnapshot
causally consistent sessions 因果一致性会话
Causal Consistency 是一种保证,指在启用因果一致性的情况下,读操作会确保在逻辑上尊重因果顺序。
在发生相关的操作时,Causal Consistency 能确保:如果有依赖关系,读操作不会早于依赖的写操作完成。
MongoDB 默认不开启因果一致性,但可以通过 API 显式启用。
eg: 如果 A 写入了数据,随后 B 读取了数据,在因果一致性中,B 应该总是能看到 A 的写操作结果,而不会读到那个写入之前的快照。
local
readConcern 的默认级别。
local 仅从主节点读取本地数据,这些数据已经过一些基本的同步,且不会读取到孤立文档。
local : 返回实例中的数据,不保证返回的数据被写入大多数副本集成员。(返回的数据可能会被回滚)
使用前提(任何情况)
- 单独使用
- 开启了因果一致性会话
causally consistent session - 开启了事务
transactions
available
available 适用于对实时场景非常高的情况。
使用前提:
- 没有开启
causally consistent session和transactions的会话。 (即无法在causally consistent session和transactions的会话中使用) - 仅适用于
sharded clusters
对于 sharded clusters , available 提供了最低延迟的读取。
- 不需要等下多少票确认
- 直接从当前在线节点返回数据
- 读取逻辑简单,无需进行额外的状态检查或锁定
majority
对于与多文档事务无关的读取操作, majority 读取的数据已被副本集的大多数成员确认。(读取的文档是持久的,并保证不会被回滚)
CURD Concepts (CURD 概念)
原子性和事务
https://www.mongodb.com/docs/manual/core/write-operations-atomicity/
MongoDB 在单个文档上的修改是原子性的。
当单个操作修改多个文档时,每个文档的修改是原子的,但是整个操作不是原子的。(操作可能会交错进行)
如果需要原子性读取/写入多个文档时,MongoDB z支持分布式事务。(distributed transactional)
分布式查询
Replica Sets
默认情况下,Client 从 Replica Sets 的 primary 节点 读取数据。
但是 Client 可��以通过指定 read preference (读取偏好)将读取请求导向到其它节点。

在 replica sets 中,所有的写操作都会发送到 primary 节点中。 primary 节点应用写操作并将操作记录在 primary 节点的操作日志或
oplog 中。

sharded clusters


Causal Consistency 因果一致性
如果一个操作在逻辑上依赖于前一个操作,那么这些操作之间存在因果关系。
Query Optimization 查询优化
索引通过减少查询操作需要处理的数据量来提高读取操作的效率。
创建索引
// 在 type 上查询
db.inventory.find( { type: typeValue } );
// 在 type 字段上创建索引 , 1 表示升序
db.inventory.createIndex( { type: 1 } )
Query Selectivity 查询选择性
查询条件能够有效地从集合中排除或过滤掉文档。
Covered Query 覆盖查询
覆盖查询是一种可以完全使用索引来满足的查询,而不需要检查任何文档。
- 查询中的字段都是索引的一部分
- 结果中返回的所有字段都在同一个索引中
- 查询中没有字段等于 null. 例如
{"field":null}{"field":{ $eq : null }}
案例:
db.inventory.createIndex( { type: 1, item: 1 } )
db.inventory.find(
{ type: "food", item:/^c/ },
{ item: 1, _id: 0 } // 为了使用索引覆盖查询,必须指定 _id: 0 以从结果中排查 _id 字段(因为索引不包含 _id 字段)。
)
Embedded Documents
索引可以覆盖对嵌入文档中字段的查询。
db.userdata.createIndex(
{ "user.login": 1 }
)
db.userdata.find(
{ "user.login": "tester" },
{ "user.login": 1, _id: 0 }
)
慢查询
查询 mongodb 的性能
- $currentOp 查询有关活动操作和游标的信息
- top 获取额外的操作计数和延迟统计信息
- serverStatus 查询执行的性能问题和异常
- $queryStats 常见查询分片的信息,提供了运行的查询类型的整体视图。
- $indexStats 查询索引统计信息
慢查询分析
- system.profile , 启用后,数据库分析器会将有关慢查询的信息存储在 system.profile 集合中。
- db.collection.explain() 查询计划和执行统计信息。
执行高级查询分析
- $planCacheStats 返回有关集合计划缓存信息。 查询计划器(query planner) 使用这些计划来高效的完成查询。
查询计划 query plan
db.collection.explain().find()db.collection.find().explain()Explain plan results- 查询所需时间
- 是否使用了索引
- 扫描的文档和索引的数量
verbosity mode
- queryPlanner
- 默认值
- 返回了 winning plan 的信息
- 不会实际执行查询,只是显示查询计划
- executionStats
- 执行查询并提供 winning plan 的详细执行统计信息(不会显示被拒绝的计划的执行统计)
- 查询计划
- 执行时间
- 文档扫描数量
- 索引条目扫描数量
- 返回文档数
- 内存使用情况
- allPlansExecution
- 不仅显示 winning plan ,还会显示所有被考虑的计划。
- 实际执行查询,并提供每个计划的执行统计信息。
- 显示了更多执行细节
- 所有被评估的计划
- 每个计划执行时间
- 每个阶段处理的文档数量
- 内存使用情况
结果分析
具体字段含义见官网:https://www.mongodb.com/docs/manual/reference/explain-results/
queryPlanner.winningPlan.stage
COLLSCAN表示集合扫描,必须逐文档扫描整个集合(全文扫描)IXSCAN表示使用了索引。FETCH检索文档GROUP分组文档SHARD_MERGE合并来自分片的结果SHARDING_FILTER过滤掉来自分片的孤立文档TS_MODIFY修改时间序列集合BATCHED_DELETE用于内部批处理的多个文档删除EXPRESS适用于一组有限的查询
-
executionStats.nReturned返回文档的总数 -
executionStats.totalKeysExamined扫描到的索引条目(index entries),0 表示未使用索引。 -
executionStats.totalDocsExamined扫描的文档总数。